International Space Station:
The International Space Station (ISS) is a multi-nation building venture, that is the greatest single structure human beings ever put into space. Its principal development was once accomplished between 1998 and 2011, though the station always evolves to consist of new missions and experiments. It has been always occupied for almost 20 years, that is since November 2, 2000.
As of January 2018, 230 persons from 18 international locations have visited the International Space Station. Top collaborating nations consist of the United States (145 people) and Russia (46 people). The time of astronauts and research on the space station is allotted to space companies according to resources and money (such as modules or robotics) that they contribute.
The ISS consists of contributions from 15 nations: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia) and the European Space Agency (ESA) are the essential companions of the space station who made a contribution most of the funding; the different companions are the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
The operations for the space station to be operated through at least 2024, with the companions discussing a viable extension till 2028. Afterwards, the space station may want to be deorbited, or recycled for future space stations in orbit.
Crews aboard the ISS are assisted with the aid of mission control facilities in Houston and Moscow and a payload control center in Huntsville, Ala. Other worldwide mission control facilities aid the space station from Japan, Canada and Europe. The ISS can additionally be managed from mission control facilities in Houston or Moscow.
Altitude of ISS:
The space station flies at an common altitude of 248 miles (400 kilometers) above Earth which is a Low Earth Orbit. It circles the globe each and every 90 minutes at a pace of about 28,000 km/h. In one day, the station travels about the distance it would take to go from Earth to the moon and back.
The space station appears as a brightened star throughout the night time in the sky. Even without telescope it can be seen at the night sky.
Construction of ISS:
The International Space Station was once taken into space piece-by-piece and progressively constructed in the orbit by spacewalking astronauts and robotics. Most missions used NASA's Space Shuttle to raise up the heavier pieces, even though some individual modules had been launched on single-use rockets. The ISS consists of modules and connecting nodes that include residing quarters and laboratories.
Some of the different main modules and elements are as follows:
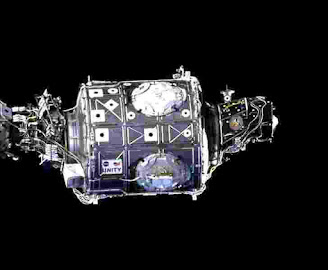
Zarya:
Zarya, additionally recognized as the Functional Cargo Block or FGB, is the first module of the ISS to be launched. The FGB supplied electrical power, storage, propulsion, and instruction to the ISS all through the preliminary stage of assembly. Mainly Zarya is presently used for storage, each interior the pressurised part and in the externally installed gas tanks. The Zarya is a descendant of the TKS (Transport Supply Spacecraft) designed for the Russian Salyut Programme. Although it used to be constructed by means of a Russian company, it is owned by US.
Zarya was constructed from December 1994 to January 1998 at the Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center (KhSC) in Moscow.
Zarya was once launched on 20 November 1998 on a Russian Proton Rocket from Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 81 in Kazakhstan to a 400 kilometres excessive orbit with a designed lifetime of at least 15 years. After Zarya reached orbit, STS-88 launched on December 4, 1998 to connect the Unity module.
Unity:
The Unity connecting module, additionally recognized as Node 1, is the first US-built aspect of the ISS. It connects the Russian and US segments of the station. This is the place where crews eat foods together.
This module is cylindrical in shape, with six berthing areas (forward, aft, port, starboard, zenith, and nadir) facilitating connections to different modules. Unity measures 4.57 metres in diameter, 5.47 metres long, made of steel, and used to be constructed for NASA through Boeing in a manufacturing facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Unity is the first of the three connecting modules; the other two are Harmony and Tranquility.
Unity used to be carried into orbit as the most important cargo of the Space Shuttle Endeavour on STS-88, the first Space Shuttle mission devoted to meeting of the station. On 6 December 1998, the STS-88 crew mated the aft berthing port of Unity with the ahead hatch of the orbiting Zarya module. This used to be the first connection made between two station modules.
Zvezda:
Suggested Articles
Destiny:
Quest:
Pirs and poisk:
Harmony:
How to spot the station
Tranquility:
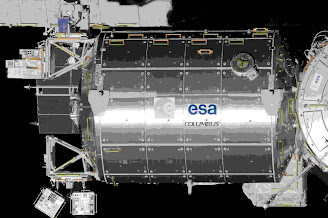
Columbus:
Kibo:
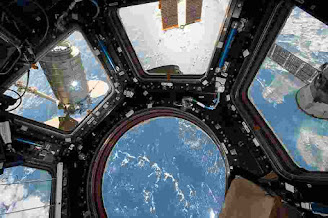
Cupola:
Rassvet:
Leonardo:
Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM):
International Docking Adapter (IDA):
Robotic arms and cargo cranes:
International Space Station size:
The size of the space station, together with its giant photovoltaic solar arrays, is equal to the area of a US football field,, and weighs almost 391,000 kilograms, no longer which includes travelling vehicles. It now has greater livable room than a traditional five-bedroom house, and has two bathrooms, health club facilities and has a 360-degree bay window.
Crews and their activities in space:
The ISS typically holds crews of between three and six humans. But crew sizes have diverse over the years. After the Columbia space shuttle catastrophe in 2003, crews had been as less as two humans due to the decreased capability to launch humans into space on the smaller Russian Soyuz spacecraft. The ISS has additionally housed as many as thirteen humans quite a few times, however solely for a few days at some point of crew changeovers or space shuttle visits.
The Space Shuttle fleet retired in 2011, and after that Soyuz was the solely modern-day approach to deliver human beings to the ISS. Three astronauts fly to the space station in Soyuz spacecraft and spend about six months there at a time. If the crew wishes to evacuate the station, they can return to Earth aboard two Russian Soyuz vehicles docked to the ISS.
From the beginning of 2019 or 2020, some private companies came forward to support the space competition such as the business crew automobiles Dragon (by SpaceX) and CST-100 (by Boeing). Those were anticipated to extend ISS crew numbers due to the fact they can deliver up greater astronauts at a time than Soyuz.
Astronauts spend most of their time on the ISS performing experiments and maintenance, and at least two hours of each day are allotted for exercising and private care. They additionally sometimes perform spacewalks, media/school activities for outreach, and submit updates to social media.
The ISS is a long-term research platform for human health. Now it is considered as a key stepping stone to let people do research and discover new things in space. Human bodies change in microgravity, which includes modifications to muscles, bones, the cardiovascular system and the eyes; many scientific investigations are still occuring to symbolize how extreme these conditions are and whether or not they can be reversed.
Astronauts additionally do organic experiments, such as on rodents or plants, which the astronauts can make them grow and now and again consume in space.
However, only science experiments are not done in there, the space station should also be maintained. Sometimes, to repair the station they had to do spacewalk.. From time to time, these repairs could be emergency. One incident happened with astronaut Luca Parmitano when his helmet stuffed with water during his work backyard the station. NASA now responds rapidly to water incursion incidents. It additionally has introduced pads to the spacesuits to soak up the liquid, and a tube to furnish an alternate respiratory vicinity have to the helmet fill with water.
NASA is additionally trying out engineering solution that could complement or change astronaut spacewalks. One example is Robonaut. It is a prototype designed and built in Johnson Space Center, NASA. It was designed to perform the dangerous works in space to reduce the risks of the crews.
Spacecrafts used for ISS:
Besides the space shuttle and Soyuz, the ISS has been visited by using many different types of spacecrafts. Uncrewed Progress (Russia) cars make everyday visits to the station. Europe's Automated Transfer Vehicle and Japan's H-II Transfer Vehicle used to do visits to the ISS as well, till they had been retired.
NASA started growing industrial cargo spacecraft to the space station beneath the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services Program, which lasted from 2006 to 2013. Starting in 2012, the first business spacecraft, SpaceX's Dragon, made a go to to the space station. Visits proceed these days with Dragon and Orbital ATK's Antares spacecraft underneath the first stage of NASA's Commercial Resupply Services program. Thus, SpaceX became the first private company to resupply the ISS and also it became the first company to fly humans in ISS on 31 May, 2020.
Purposes of ISS:
- Scientific research.
- Exploration.
- Education and cultural outreach.
- To attract the young generation towards research.
- To open the door for future space travel.
- Human space exploration.
























0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box..