Avionics Technology: All you should know
Avionic Technology is the electronic system technology used in aircrafts, satellites and spacecrafts for controlling, navigation, communication, display and hundreds of things that are supposed to be included in air vehicles. The term Avionics is the combination of Aviation and Electronics.
History of Avionics Technology:
The concept of aircraft may has been almost a century but the avionics has been almost for more than 2000 years. This is obviously not a little time. According to history, kites were the first generation of modern aircrafts. Even, Leonardo da Vinci made many models of aircrafts. By observing his drawings, we can easily guess about his thinking capability. Vinci introduced that object which did not even exist at that time.
The modern avionics technology suddenly grew up after the successful testing of first aircraft designed by Wilbur Wright and Orville Wright.
The term Avionics was first introduced by an American Journalist and UFO researcher Philip J. Klass. The journey of modern avionics technology was first began in World War II. The autopilot system which is very common technology for today was first began for bombing a targeted area with bomber planes from a very high altitude.
Sectors of Aviation Industry:
There are two sectors of aviation industry. They are-
Military:
The aircrafts which are flown by nation's air force or in spacecrafts and not available for commercial applications.
Civil:
The aircrafts which fall under this sector are available for commercial applications. It is also divided by two types-
Domestic:
The flights which start and end within the border of the same country are called Domestic flights.
International:
Avionics Technology of aircraft:
The location of the electronic system of an aircraft is the cockpit, which includes flight control, communication, navigation, weather, anti-collision system etc. For powering the avionic system of the craft, mostly 14 or 28 Volt DC electrical system is used. But for some specific purposes like airliners or military combat aircrafts uses AC electrical systems operating at 400 Hz and 115 Volt of AC. The whole avionics technology consists of following systems.
Communication:
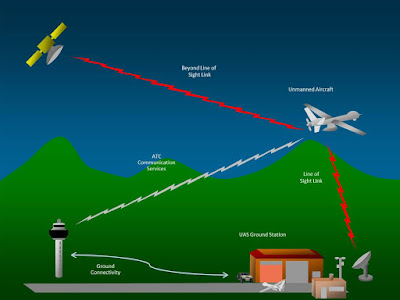
Communication is the major part of avionics technology. Communication mainly connects the flight deck to the ground station and flight deck with the passengers.
The aviation communication systems works on the airband of 118-136.975 MHz of VHF (Very High Frequency) wave of radio spectrum. Phonetically, it is also called as Victor. The VHF is also used in line of sight communication like aircraft to aircraft or aircraft to ATC (Air Traffic Control). For communication, AM (Amplitude Modulation) is used and the conversation is performed in Simplex mode. Simplex communication is the channel in which transmission of information takes place only in one direction).
Air navigation:
In Avionics, navigation is the determination of location and position on or above the surface of the earth. The basic principle of air navigation includes planning, recording and controlling the craft from one place to another.
Avionics Technology uses satellite navigation systems like GPS and WAAS (Wide Area Augmentation System), INS (Inertial Navigation System), Radio Navigation system like VOR (Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range) or LORAN (LOng RAnge Navigation)etc.
Radio Navigation is older navigation system used earlier times where the pilot had to plot the intersection of the signals on a paper map for determining an aircraft's location. But, now the modern navigation systems like GPS calculate the position automatically and display it to the crew in a digital moving map.
Displays or monitors:
Before 1970s, in aircraft cockpits there used electromechanical displays, gauges and instruments. But in 1970, when CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) was first introduced after then, "Glass Cockpit" became popular. Glass Cockpit refers to the use of computer displays instead of traditional analog displays. After that, more number displays, dials and instruments were being added progressively time by time.
Flight control system:
A necessary part of modern day aircrafts are autopilot mode which was invented during World War I for bombing targeted areas using bomber planes. Nowadays, most commercial aircrafts are equipped with aircraft flight control system to reduce pilot error or workload at landing or take off.
Fuel system:
Fuel Quantity Indication System (FQIS) monitors the amount of fuel used in the craft. Using various sensors like capacitance tubes, temperature sensors, densitometers & level sensors, the FQIS computer calculates the mass of fuel remaining on board.
Fuel Control and Monitoring System (FCMS) reports fuel remaining on board in a similar manner. However, by controlling pumps & valves, also manages fuel transfers around various tanks.
Collision Avoidance System:
To supplement ATC, most large transport aircraft and many smaller ones use a Traffic alert and Collision Avoidance System (TCAS), which can detect the position and location of nearby aircrafts, and provide instructions for avoiding a midair collision.
For avoiding Controlled Flight Into Terrain (CFIT) (it is an incident when, an aircraft under pilot control flies into the ground, mountain, a body of water or an obstacle) aircrafts use systems like Ground Proximity Warning Systems (GPWS). The major weakness of GPWS is the lack of "look-ahead" information, because it only provides altitude above terrain "look-down". To overcome this weakness, modern aircraft use a Terrain Awareness Warning System (TAWS).
Flight Recorders:
For storing or recording the flight information and audio from the cockpit, Black Boxes are commercially used. Those informations are often recovered from the black boxes of an aircraft after a crash to determine control settings and other parameters during the incident.
Weather systems:
For aircrafts flying at night or in instrument meteorological conditions, where it is not possible for pilots to see the weather ahead, some weather systems like weather radar and lightning detectors are very very important .
For light aircrafts, some lightning detectors such as Stormscope or Strikefinder are more practical due to low cost. Through satellite data connections, the pilot can see the weather condition of far beyond the range of their in flight systems. Nowadays, modern displays allow weather information to be integrated with digital moving maps, terrain, and traffic onto a single screen, greatly simplifying navigation.
Mission Avionics:
For military applications, different aircrafts are used and those crafts are called as Military Aircrafts. Such aircrafts are designed to deliver weapon or to attack on enemy with bombs. Thus, military aircrafts are grouped as Fighters, Bombers, Attack, Electronic Warfare, Maritime Patrol, Multirole etc.
Technologies used in Military avionics are given below-
Military Communication:
Though aircraft communication is used for safe flight, to secure the communication, some tactile systems are designed to cope up in some serious situations like battlefield. The UHF (Ultra High Frequency), VHF (Very High Frequency), satellite communication system combined with ECCM (Electronic Counter CounterMeasures) and cryptography secure the communication of the aircrafts.
RADAR:
The full form of RADAR is RAdio Detection And Ranging which is a system that uses radio waves to determine the range, angle or velocity of any object. A radar system consists of a transmitter which produce electromagnetic waves in radio or microwave domain, a receiver, transmitting antenna, receiving antenna and processor to determine the properties of the objects. The radio waves are transmitted from the transmitting antenna, reflect off the object and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects.
SONAR:
The full form of SONAR is SOund Navigation And Ranging. It is a system or technique that uses sound waves to navigate, communicate or detect other objects. In avionics, the maritime aircrafts can drop active and passive sonar devices which can also detect enemy submarines.
Electro-optics:
In avionics technology, electro-optics include Head Up Display (HUD), Forward looking InfraRed (FLIR), InfraRed Search and Track (IRST) and other passive infrared sensors. These devices are used to provide visualization of detailed information to the crew members on display.
ESM/DAS:
ESM (Electronic Support Measures) and DAS (Defensive Aid Suit) are used to collect information about possible and incoming threats. These sub systems can be used to launch devices (even automatically) to counter the incoming threats against the aircraft.
These are basically different parts of avionics technology. Actually, it is a very broad subject and each part of above mentioned is a complete long course. Here, I have just tried to introduce with the concept of avionics technology.










0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box..